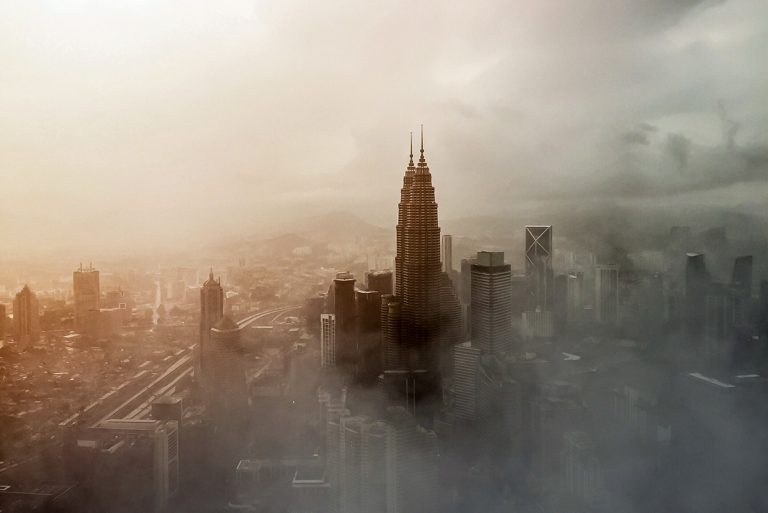
For many people worldwide, the air they breathe is a silent killer. Air pollution is a long-standing environmental issue that deteriorates human health and the environment. In this article, we share 30 facts that show just how serious air pollution is, the key sources of air pollution, and its devastating effects on our world.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution is the contamination of air with a range of substances that can harm human health, damage the environment or alter climatic conditions. This pollution may be indoor air pollution, within enclosed spaces, or outdoor air pollution affecting the wider environment. Contributing substances include glasses, particulates, organic and inorganic molecules, and organisms.

The sources of air pollution are diverse and not necessarily all man-made. For example, wildfires and volcanic activity contribute to net air pollution. However, industrial activity has been a key driver of this problem over the past 200 years.
30 need-to-know facts about air pollution
Here are 30 important air pollution pacts everyone should know. These facts and references show the impact of air pollution and the range of its negative effects.
1. Clean air is a human right
In August 2022, the United Nations declared a healthy environment to be a human right, including the right to breathe clean air. The UN considers air pollution to be a threat to humanity’s future and a significant contributor to environmental degradation.
This resolution is not legally binding, but the UN hopes that this resolution will spur member nations to address air pollution in their domestic policy and legislation.
2. Over 99% of the Earth’s population breathes polluted air daily
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 99% of the world’s population is exposed to polluted air. The main cause is the burning of fossil fuels for power, vehicular transport, and industry, with developed countries being big contributors.
3. More than 10 percent of deaths worldwide are attributable to air pollution-related disease
According to Our World in Data, air pollution contributes to 11.65% of deaths across the globe. This is because air pollution raises the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory disease, diabetes, stroke, and lung cancer.

This staggering proportion of air pollution-related deaths is unequally distributed, with the greatest numbers of deaths from the ir-pollution-related disease in Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and South Eastern Asia.
4. Air pollution cuts life expectancy by up to 3.5 years
Current global air pollution levels are thought to be responsible for an average reduction in life expectancy of one year and eight months, and as much as three and a half years in the worst-hit regions.
A drop in life expectancy reflects the pernicious effects of air pollution on health and well-being. Health experts currently consider air pollution more of a threat to life expectancy than war, smoking, or HIV.
5. Low and middle-income countries have the highest rates of air pollution-related deaths
Mortality related to air pollution is most marked in low to middle-income countries. In 2019, air pollution caused 1.85 million deaths in China, the highest number in the world, and 1.67 million in India.

The difference in severity is because of high rates of indoor air pollution caused by cooking with solid fuels. Over 2.6 billion people rely on kerosene and biomass for cooking and heating, with poor ventilation and indoor air quality. The transition to industrialization is also a big contributor to unregulated air pollution.
6. Up to 80% of air pollution-related deaths could be preventable
According to the WHO, the vast majority of air pollution-related deaths are preventable. They believe that a global reduction of air pollution levels to the limits set out in their guidelines could prevent almost 80% of these deaths.
7. China has the greatest number of coal-fired power stations on Earth
China has the most coal-fired power stations in the world. According to Statista, mainland China has over 1,100 operational coal-fired power stations. This is just under four times the number of coal-fired power stations the second and third-ranking countries, India, and the United States, have.
And China is continuing to build coal power plants and blast furnaces with a further 43 planned in the coming years.
8. India has 10 of the world’s most polluted cities
The World Air Quality Report reports that 10 out of 15 of the world’s most air-polluted cities are in India. The following cities have some of the highest suspended particulate matter concentrations on Earth, exceeding WHO guideline limits by over 500% in some cases:
- Bhiwadi – the world’s most polluted city in 2021
- Delhi
- Ghaziabad
- Jaunpur
- Peshawar

Source: Wikimedia / wili hybrid
Air pollution in urban India is attributed to waste burning, traffic, and heating and cooking fuels. The Indian government is seeking to tackle this problem with its National Clean Air Programme, which has the target of a 30% reduction in air pollution by 2024.
9. London’s air quality is some of the worst in Europe
London, UK has some of Europe’s dirtiest air, leading to heavy health and financial consequences for its 8 million residents. According to Friends of the Earth, London’s air pollution is responsible for more than 9,000 premature deaths annually. In addition, London is Europe’s worst city for health costs regarding air pollution, at more than £1,175 for each resident.
10. In some parts of London, it only takes a few days to breach annual air pollution limits
Traffic-related air pollution is so bad in some parts of central London that annual air pollution limits are breached within a week. In January 2017, nitrogen dioxide levels on Brixton Road in London, exceeded EU air pollution limits 19 times within the first five days of the year.
11. None of the largest cities on Earth can meet air pollution limits set by the WHO
The WHO issued stringent air pollution guidelines in late 2021, tackling the particular problem of particulate matter (PM2) air pollution. Despite this initiative to improve air quality by lowering limits for PM2 nitrogen dioxide by almost 75%, an analysis by Greenpeace has shown that no major world city has met them.

Source: Wikimedia / mattbuck
12. Air pollution negatively impacts child development
Polluted air is so prevalent that it is affecting child health. Already, today’s generation of children may not breathe clean air until the age of eight years. This has major implications for their lung and cardiovascular development. Air pollution also harms fetal development in a similar way to smoking with a rise in the incidence of preterm labor.
13. Traffic-related air pollution is associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
The National Toxicology Program of the US Department of Health and Human Services has found that exposure to traffic-related air pollution, or TRAP, by living near major roads is associated with blood pressure changes during pregnancy. The research identified published studies that associated TRAP with pregnancy conditions like gestational hypertension, and pre-eclampsia.
14. The most dangerous air pollution is particulate matter
Particle air pollution is the most harmful to human health. This pollution consists of fine particles suspended in the air and includes a range of substances like:
- inorganic matter
- metals
- dust
- acid salts (e.g. sulphuric acid)
- soot (carbon)
- biological materials
The smallest particles are invisible to the human eye. These are the most dangerous as they can penetrate the lung deeply and precipitate or worsen respiratory or cardiovascular disease.

Source: Wikimedia / Environmental Protection Agency
15. PM 2.5 air pollution has particles of 2.5 microns or smaller
PM 2.5 is a special category of particle air pollution with particulates that are so tiny that 25,000 of them would fit in an inch! This ear-invisible air pollution gives the sky a hazy appearance when levels are high. These particles cause pernicious short-term and long-term health effects including eye, nose, and respiratory tract irritation with shortness of breath.
Environmental and public health authorities like the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) carefully monitor PM 2.5 levels to ensure they comply with air quality standards. If levels are raised, they will alert the public so that people with cardiovascular and respiratory health problems can avoid or minimize their exposure to them.
16. Ground-level ozone harms human health and vegetation
Unfortunately, ozone is not just limited to the UV-absorbing ozone layer. It is also generated at ground level (tropospheric ozone) and can harm human health. Nitrogen and sulfur oxides react in sunlight to create ozone-rich smog. Ozone generation is associated with traffic and industrial emissions and worsens on sunny days.

Source: Wikimedia / DANMUSISI
Ozone in air pollution is a respiratory irritant, provoking conditions like asthma on hot sunny days when ozone levels are high. Young growing plants are also sensitive to ozone and can become damaged. Authorities carefully monitored levels of ozone with legislation and initiatives in place in many countries to limit levels.
17. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in air pollution raise cancer risk
PAH are cyclic hydrocarbon compounds that contain multiple fused benzene rings. They are particulates that are primarily produced by the burning of fossil fuels in vehicles, heating and cooking, or agricultural waste. People who are exposed to these pollutants through inhalation skin contact or ingestion.
The WHO has found that prolonged exposure to PAH in air pollution is associated with a raised risk of several cancers, including breast and lung cancers.
18. See that orange haze over the skyline? That’s nitrogen dioxide!
An orange haze in the sky indicates high levels of nitrogen dioxide (NO2). This is one of the most toxic forms of air pollution and can hand over a city like an orange cloud. NO2 is a respiratory irritant, causing lung inflammation and aggravating conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and COPD.

19. In the US, sulfur dioxide levels have been falling since the 1970s
Sulfur dioxide is a chemical released from the burning of fossil fuels in vehicle engines and industrial processes. SO2 is known for its negative environmental and health effects, including respiratory problems, allergies, and the damaging effects of acid rain.
In the US, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has carefully monitored SO2 emissions for decades. Levels of SO2 fell from over 32 million tons per annum to just 1.8 million tons in 2021. They attribute the precipitous drop to improved industrial practices along with stringent legislation to limit emissions levels and protect public health.
20. Air pollution affects the health of outdoor runners
Running in polluted air can harm your health. Running when the air quality is bad can lead to the development of breathing problems, particularly if you are sensitive to certain pollutants in the air. Exercising in polluted air may also harm long-term health as runners inhale deeply, drawing particulates deep into their lung tissue.
Before you go running, you can check the Air Quality Index (AQI) for where you live. A green rating (0-50) is suitable for running, levels above yellow (51-100) or orange (101-150) should be avoided.
21. Air quality varies by time of day
In urban areas, there are marked differences in air quality throughout the day. Air is cleanest early in the morning, before traffic and industrial activity gets underway. Pollution levels rise again during the evening rush hour. Ozone levels and carbon dioxide levels rise in the afternoon and early evening.
22. Diesel engine exhaust contains known carcinogens
According to The American Cancer Society, WHO, and other health authorities, diesel engine exhaust is a known carcinogen. Diesel exhaust contains gasses and particulates including harmful substances like heavy metals, nitrogen and sulfur dioxide, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).

Prolonged exposure to diesel exhaust fumes through work, driving, or recreation in polluted areas can elevate your risk of lung, bladder, and pancreatic cancer. Exposure to diesel fumes also raises the risk of childhood cancers like leukemia.
23. The number of diesel vehicles is increasing
Despite the growth in electric vehicle ownership, the proportion of diesel vehicles on UK roads is increasing. Currently, over 12 million diesel vehicles are being driven in the UK, a 13% rise in the last ten years. The increase in diesel vehicles has been driven by government incentives because of the greater fuel efficiency of diesel compared to gasoline.
24. In-car air pollution can be as harmful as passive smoking
Sitting in traffic jams for hours on end can leave vehicle occupants exposed to levels of air pollution that are equivalent to smoking several cigarettes. According to the British driving organization the RAC, the levels of air pollution are over 140% more inside a car than outside.

In-car pollution is high because exhaust fumes pass through air filters and build up inside the car. Sitting inside your vehicle for just one hour daily is equivalent to smoking 180 cigarettes over a year.
25. The economic cost of air pollution exceeds $2.9 trillion
A 2020 report by the Center for Research on Energy and Green Air found that the economic costs attributed to air pollution could be as much as 3 trillion US dollars. This is well over 3% of the global GDP. Dirty air makes places less livable and productive.
The effects of air pollution on health have contributed to 1.8 billion days off work, with a resultant loss of productivity. Millions of new childhood asthma diagnoses also lead to parental absence from work for childcare.
26. In California, USA, smoke from wildfires is a significant contributor to regional air pollution
An increasing number of severe wildfires have affected California, with 12 of the 20 worst wildfires hitting the state in the last five years. High-severity wildfires generate significant amounts of smoke with high levels of fine particulate matter.

Source: Flickr / Felton Davis
The increased frequency and severity of wildfires have led to a deterioration in air quality. The smoke contains pollutants like carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen oxide, and volatile organic compounds. In particular, fine particulate matter from smoke contributes to prolonged pollution and ongoing health effects.
27. In the US and UK, over 60 percent of car journeys are under six miles
Studies in both the UK and US have shown that almost two-thirds of car journeys are less than six miles. These short household trips contribute significantly to air pollution and often could be using public transport or on foot.
28. In Europe, almost 11 million cars cheated air pollution tests between 2009 and 2015
In 2016, a notable scandal involving Volkswagen emerged, when regulators found that millions of their cars had cheated on emission tests. Detailed investigations found Volkswagen had fitted affected diesel cars with software that enabled cars to reduce their exhaust emission in laboratory testing.
The scale of the ‘Dieselgate scandal’ has meant that up to 500,000 VW cars in the US and millions more in Europe have diesel exhaust emissions that breach US and EU emissions standards. Volkswagen received severe financial penalties, but health authorities think the air pollution generated by the cars has contributed to at least 59 premature deaths.
29. Air pollution travels
Weather patterns and wind cycles can shift air pollution across the world. This means air pollution can affect people that live far away from the locations where the pollution was generated. Sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone often travel long distances from their source, making air pollution a global problem as the worst polluters can affect everyone.
The expansive disbursement of air pollution makes limiting it even more important. Measures to reduce air pollution can improve air quality not only where the pollution is generated, but across the world.
30. Landfills are one of the largest sources of air pollution
Landfills are a leading contributor to global air pollution. As municipal waste that is dumped in landfills breaks down, it releases a range of noxious gasses. Landfills are the third largest emitter of the greenhouse gas methane. Decomposing waste also emits health-harming gasses like benzene, ammonia, nitrogen, sulfides, and ozone.

Emissions from landfills are so serious that they have now become the focus of emission standards and limits in many countries. In the United States, The Clean Air Act has been used to create Environmental Protection Agency Standards for landfill pollution.
In conclusion
As you can see, air pollution is a persistent and pernicious problem that harms humans and the environment. Tackling air pollution is challenging because key sources, like industrialization, transport, and human activities like cooking or heating a home are essential to modern life.
Even in less economically developed countries, the use of simple open fires and solid fuels is also extremely polluting, and countries that are industrializing their economic development are some of the biggest polluters.
Finding meaningful solutions to air pollution will likely combine the innovation of industrial processes to make them less polluting with changes in human activity and consumption. There are already sophisticated air scrubbing, air filtering, and pollution capture technologies and increasing awareness of this problem have motivated people to make changes that limit pollution.