Reducing worldwide water pollution is one of the greatest challenges governments and global organizations face today. Many causes of water pollution are indirectly or directly precipitated by human activity and are often difficult to resolve.
However, the stakes couldn’t be higher. In 2021, over 2.5 million acres of ponds, reservoirs, and lakes were deemed unsafe in the U.S. alone.
Water pollution can potentially damage aquatic ecosystems and human life for generations to come. More than 50 diseases are linked to poor drinking water quality, and 80% of diseases worldwide are related to poor drinking water quality.
Water pollution can lead to harmful medical conditions such as diarrhea, skin diseases, malnutrition, cancer, and even death for those, especially at risk – like children and the elderly.
Animals and plants that reside in either saltwater or freshwater environments are also increasingly affected by polluted waters. Chemicals and pollutants can impact water temperature and potentially disrupt or kill marine life unused to higher temperatures.
In this article, we’ll dive into everything you need to know on this issue, and what the most common causes of water pollution are.
What is water pollution – and why is it a problem?
Caring for our environment not only has to do with making greener shopping choices, but also preserving the natural resources that are essential to all life on Earth. In its three phases – solid, liquid, and gas – water ties together the major parts of the Earth’s climate system: air, clouds, the ocean, lakes, vegetation, and glaciers.

Water is polluted when harmful substances like chemicals contaminate a waterway. These toxic substances render the water unusable for drinking, cooking, swimming, and cleaning.
Pollutants can include anything from trash to bacteria to parasites, but there are many more causes of water pollution to be aware of.
And because our atmosphere and waters are connected through the water cycle, pollution of all kinds has the power to damage waters further.
All forms of pollution, in fact, eventually make their way into the water.
Air pollution settles onto lakes and oceans, and land pollution can seep into soil, underground waters, and eventually the ocean. Because water is considered a universal solvent, it is the most vulnerable to pollution and is able to dissolve more substances than any other liquid on earth.
Let’s dive into the bodies of water most susceptible to water pollution: groundwater, ocean water, and surface waters.
Groundwater
Groundwater exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. Underground, groundwater fills in the spaces between sand, gravel, and other rick forms. Gravity pulls water down towards the center of the earth, and it gradually fills in the fractures in rock and sediment.
Groundwater flows naturally out of these rock materials or can be drawn up to the surface, and these rock materials are called aquifers. Water flows slowly and horizontally through aquifers towards bodies of water like rivers and lakes.

Groundwater gets polluted when contaminants like pesticides, fertilizers, and waste make their way into aquifers. A large number of the world’s population uses groundwater as drinking water, so the pollution of this resource can leave thousands of people without clean drinking water.
Surface water
Surface water is any body of water found on the Earth’s surface, including saltwater and freshwater found in our oceans, rivers, streams, and lakes.
Because it is more accessible than groundwater, surface water is heavily relied on by humans around the world for drinking water and farming, in addition to the wildlife that rely on these bodies of water. In 2015, almost 80% of all water used in the U.S. came from surface water.

Spills of harmful substances can cause surface water pollution. Typically, improperly treated wastewater or an industrial operation, erosion, or runoff resulting from a rain storm is the culprit of surface water pollution. Runoff can be contaminated because it picks up pollutants from the land it flows across and deposits elsewhere.
Ocean water
The preservation of our oceans is crucial to the survival of millions of marine animals, fish, and plant species. And yet, ocean waters are some of the most extensive grounds for water pollution, most of which is caused by human activity.
80% of ocean water pollution originates on land, where it can be transported from storm drains and sewers. Pollution on the sand from single-use plastics and other waste can hurt marine life, break down over time, and dissolve in the ocean.

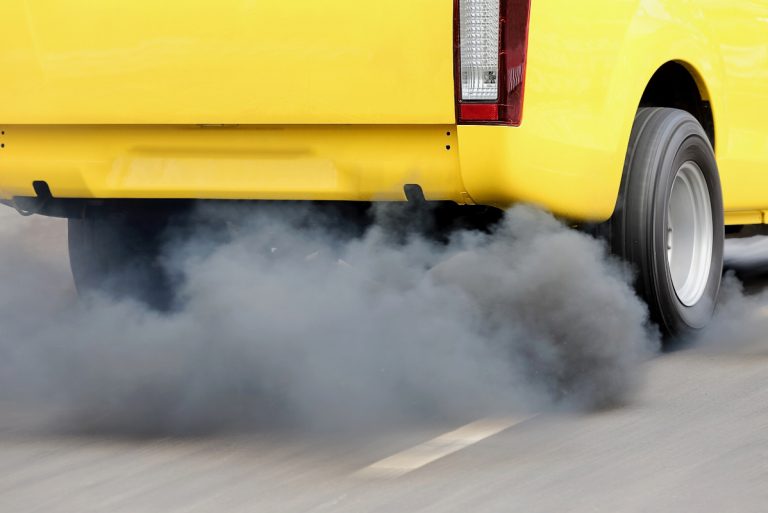
Ocean waters can also be polluted by ocean dumping, on-land machinery like cars and trucks, in addition to airplanes and boats in the ocean. Like groundwater, ocean water can also absorb chemical pollutants and agricultural runoff that damage marine life substantially.
How pollutants enter our waters
Pollutants can enter bodies of water in a few ways: point, nonpoint, and transboundary sources.
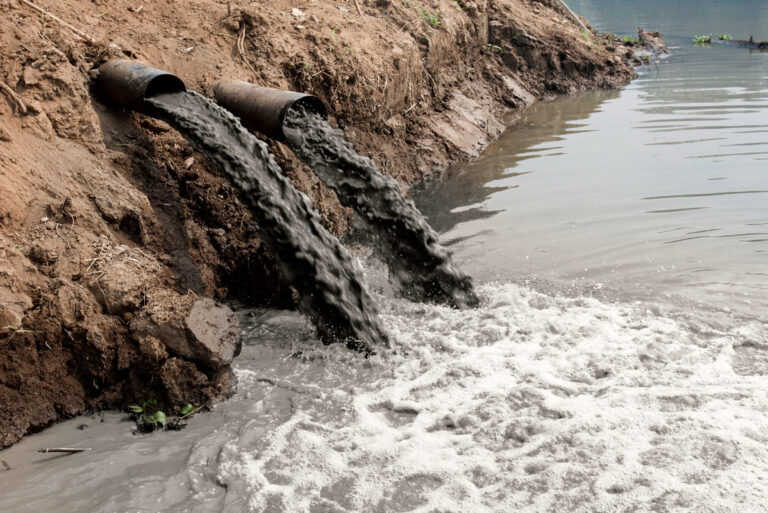
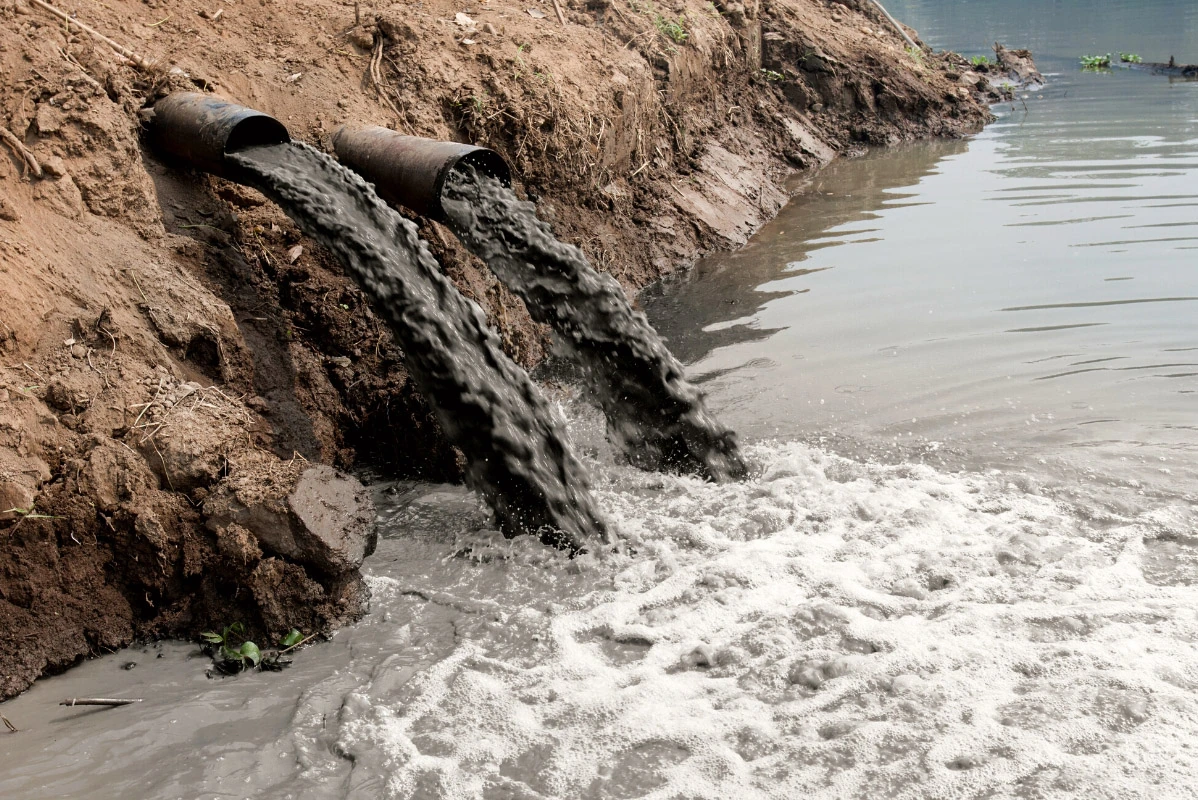
- Point source pollution is a single, identifiable source of pollution, like a pipe or a drain that deposits industrial waste into rivers and oceans. Another example of point source water pollution is a factory smokestack that emits carbon monoxide into the air, which eventually makes its way into waters.
- Nonpoint sources of pollution are harder to define. They are often described as diffuse pollution, because they refer to pollution impacts that occur over a large area and cannot be easily attributed to a single source. Nonpoint sources are often associated with the use of certain lands that contribute pollutants to air and water. Nonpoint source pollution is the leading cause of water pollution in U.S. waters, but it’s difficult to regulate, since there’s no single, identifiable culprit.
- Transboundary pollution is the result of contaminated water from one country spilling into the waters of another. Transboundary contamination can result from a disaster like a major oil spill that travels through waters.
So, what are the main causes of water pollution?
There are a large number of causes of water pollution that originate and travel to waters via a variety of different origins. Let’s understand the main causes of water pollution, and how they occur.
Sewage and wastewater
Wastewater is used water that comes from bathrooms, factories, and various commercial and agricultural activities. This wastewater usually contains harmful biological contaminants such as bacteria and pathogens. Even when the used water is treated, these contaminants can remain and still cause harm when released into other water sources.
Sewage and wastewater are released into the sea with fresh water, where the pathogens and bacteria found in that wastewater can breed disease and cause health issues in humans and animals alike.
Despite the many wastewater treatment plants that operate around the U.S. and the world, these systems are often aging and cannot handle increased capacity: each year, sewage treatment systems release more than 850 billion gallons of untreated wastewater. Each year, the impact of sewage and wastewater grows even direr.
Global warming
Rising global temperatures caused by greenhouse gasses – such as carbon dioxide emissions – heat water and reduce its oxygen content.
Just how much can greenhouse gasses raise the water temperature? Besides the water vapor naturally present in the air through evaporation, the anthropogenic greenhouse gasses retain 7% more moisture for each 1℃ (1.8℉) rise in temperature.
In addition, when temperatures rise, certain species cannot survive. Their deaths further pollute the waters. One example of this is the bleaching of coral reefs that is occurring around the world.

The rise in temperatures causes coral to reject the microorganisms that depend on it, resulting in great damage to the entire coral reefs and all the marine life that depends on it.
Agricultural operations and livestock
Often, agricultural water pollution is considered to originate from nonpoint sources. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), agricultural activities that cause pollution can include:
- Poorly located or managed animal feeding operations
- Overgrazing
- Plowing too often or at the wrong time
- Improper, excessive, or poorly timed application of pesticides, irrigation water, and fertilizer
As a result of these activities at the many farms and ranches around the U.S. and world, several pollutants are released such as sediment, nutrients, pathogens, pesticides, metals, and salts.
The United States Geological Survey reports that about a half million tons of pesticides, 12 million tons of nitrogen, and 4 million tons of phosphorus fertilizer are applied annually to crops in the continental U.S.
This massive amount of chemicals will enter into and pass through every water system component, including our air, soil, streams, wetlands, and of course, groundwater.
There are several techniques that farms can utilize to mitigate these effects, such as Integrated Pest Management (IPM) which encourages natural barriers and limits pesticide use.
Fuel spillages
Fuel spillages and dumping is another of the primary causes of water pollution globally. Though disastrous accidental oil spills come to mind, like the 1991 Gulf War Oil Spill that resulted in 240 million gallons of oil spilled, damaging materials can contaminate the ocean in several different ways.
Every year, it is estimated that more than 1 million gallons of oil contaminate our oceans. Oil leaks and spills can happen in many ways, whether it be by accident while mining oil from the Earth or from oil rig malfunctions. When oil spills occur, they often kill thousands of marine life species at once.
The damage inflicted by oil spills is usually impossible to truly resolve.

Source: Wikimedia / kris krüg
Aside from oil leaks and spills, the dumping of contaminated, toxic waste material into the ocean is another large cause of water pollution. These toxic materials include dredged material, industrial waste, sewage sludge, and radioactive waste.
In addition to marine dumping, land-based sources of fuel and toxic chemicals also play a huge part in water pollution. Runoff carries fuels from factories, farms, and cities into the ocean.
Industrial operations
Industrial operations at sites around the world are major causes of water pollution. Because many industrial sites produce toxic chemical waste and pollutants, these materials can easily sink into soil, and waters that lead directly to oceans or lakes.
The toxic chemicals in the waste produced by industrial operations not only have the potential to make water unsafe for human consumption, they can also cause the temperature in freshwater systems to change, making them dangerous for many water-dwelling organisms.
A prominent example of industrial wastewater pollution comes from mining: mining has impacted thousands of miles of streams and rivers throughout the eastern and western U.S. due to active and historic mining of iron, copper, lead, gold, platinum, silver, and other materials.
Deforestation
You may be thinking – what does deforestation have to do with water pollution? Deforestation is actually one of the main causes of water pollution, and if our forests continue to be cut down, our waters will suffer.

When rainfall, runoff, or wind detaches soil particles, erosion occurs. However, healthy forests can act as a sort of filter to keep pollution out of water, anchoring soil against erosion and helping the forest absorb nutrients, according to the World Resources Institute.
Thus, when forests are disturbed, sediment can flow more easily into streams and bodies of water. Toxic materials are picked up and carried with these sediments into water, polluting it further.
In addition, forests provide drinking water to more than 33% of the largest cities in the world. The quality and existence of clean drinking water is essentially linked to forests.
Radioactive substances
Radioactive waste is a byproduct emitted from nuclear reactors, fuel processing plants, as well as hospitals and research facilities that use radioactive materials for research and treatments. Radioactive waste is also generated while decommissioning and dismantling nuclear reactors and other nuclear facilities.
Unfortunately, radioactive waste can remain present in the environment for thousands of years. When radioactive wastes are dumped in bodies of water, they contaminate the waters and can damage water supplies and human health.
Radioactive contamination is more prevalent in groundwater as compared to surface water because it is more exposed to the radioactive elements that naturally occur in rocks and magma.

Maritime traffic
According to ocean conservation non-profit Oceana, over 90% of world trade is carried across the world’s oceans by some 90,000 marine vessels. Whether for consumer or commercial purposes, these ships emit greenhouse gasses that significantly contribute to climate change.
In fact, the total international carbon emissions from ocean-going shipping in 2018 was estimated to be a massive 1,056 million tonnes. In addition, much of the plastic pollution in the ocean comes from fishing boats, tankers, and cargo shipping.
Organizations like Oceana have made recommendations to curb the global carbon emissions from maritime traffic, one of the main causes of water pollution. Some of their suggestions for shipping fleets is to take technical and operational measures like speed reductions, weather routing, and fuel switching.
Final thoughts on the causes of water pollution
Reducing water pollution is essential to mitigating climate change for generations to come.
The causes of water pollution, from industrial operations to radioactive waste and wastewater dumping, are causing serious damage to aquatic and human life around the world.
If global organizations, governments, and industries do not take certain measures to curb their release of toxic pollutants into the atmosphere, soil, and water, the effects of water pollution will continue to damage our planet.
Keen to learn more? Here are 20 facts about water pollution that may surprise you.